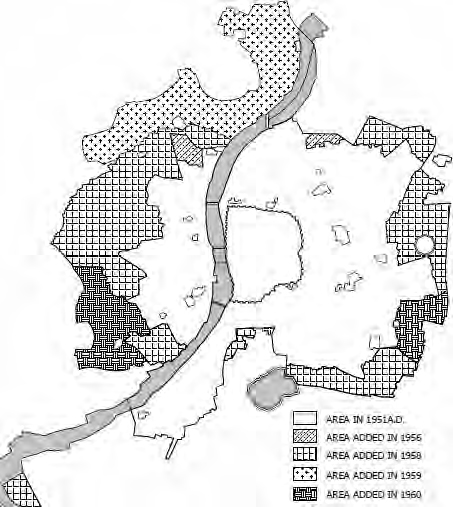
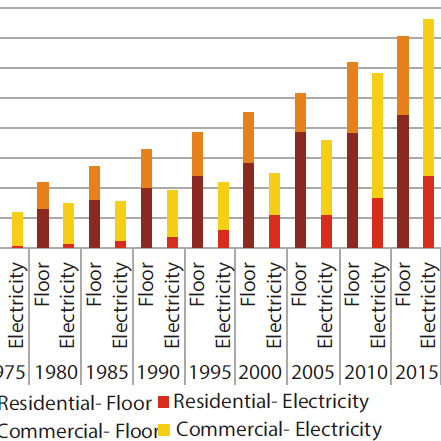
Energy savings by Energy Conservation Building Code (ECBC) implementation with regards to estimation of floor space at city level had been a challenge. Precise understanding of current floor space stock along with its historical growth pattern can help estimate floor space at city level. The study attempts to evaluate present floor stock at city level with the help of tax data base.

Extreme heat adversely affects human health and day-to-day activities. It inhibits the physiological processes by restricting the bodily heat, leading to the rise of core body temperature and water loss to perspiration. It is crucial to equally prioritize energy efficiency, thermal comfort, and indoor air quality when addressing the global cooling challenge.
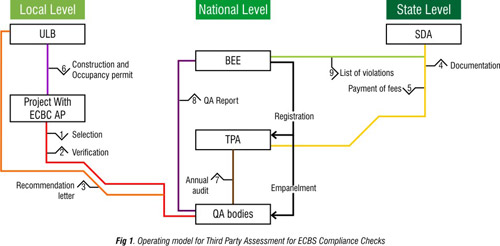
Background: The Bureau of Energy Efficiency (BEE), India, launched the Energy Conservation Building Code (ECBC) in 2007. In order to achieve significant compliance and subsequently, higher energy savings, the code must be adopted by the states and enforced by local governments. However, government and public sector agencies currently do not have the manpower or expertise to enforce ECBC. It is, therefore, crucial to build capacity and create a cadre of professionals outside the public sector.

The Asian Development Bank (ADB) assigned Center for Advanced Research in Building Science and Energy (CARBSE) to support green building ecosystem in the affordable housing sector in India, in coordination with IIFL Home Finance Limited (IIFL Home Finance), a private sector housing finance company with a strategic focus on green affordable housing.

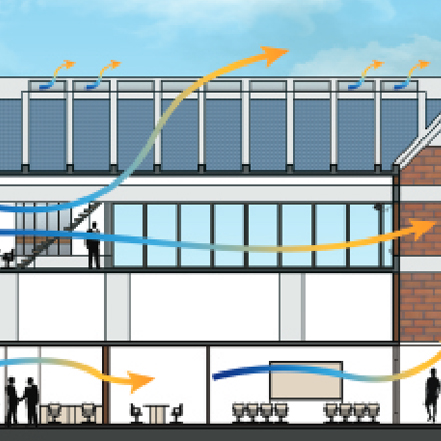
Sustainable urbanization requires the provision of secured energy for health & comfort. The Key to planning sustainable energy services is how energy demand changes over time, space and tools to help plan its reduction & generation.

The Global Innovation Initiative (GII) was a commitment between the United Kingdom and the United States of America to strengthen research collaboration between universities in the UK, USA, and emerging economies of Brazil, China, India and Indonesia. In consistent with the vision set by the UK Prime Minister David Cameron and USA President Barak Obama in joint statements signed in 2011 and 2012, GII was initially announced in 2013.
Shakti Sustainable Energy Foundation (SSEF) was established in 2009 to facilitate India’s transition to a sustainable energy future by promoting policies that encourage energy efficiency as well as the increased generation of renewable energy. Energy efficiency is a key component of Shakti’s strategy. With support received from SSEF, CEPT University has worked on various projects in the field of energy efficiency.
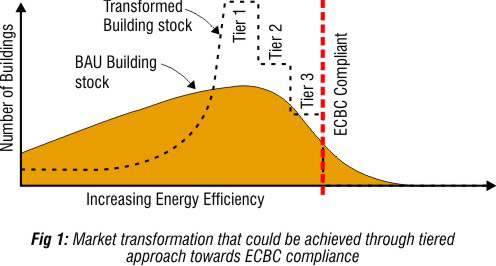
Background: The Bureau of Energy Efficiency (BEE), India, launched the Energy Conservation Building Code (ECBC) in 2007. Through mandatory compliance with the ECBC, India can achieve estimated annual energy saving of 1.7 billion kWh. The rate of compliance with the code is predicted to reach 65% by 2017.

Building simulations and energy calculations based on detailed modeling form an extremely important tool for design and investigation of energy efficient buildings. Various building components and building forms can be tested for their performance to help for the design right at the start as well as analyze the performance of an existing building.
In the absence of space conditioning standard contextual to Indian context, the space conditioning systems for buildings are designed based on ISO and ASHRAE thermal comfort standards. Field observations have indicated that these systems often operate at 22.5 ± 1°C (72.5°F ± 1.8°F) all year round without adjusting to comfort needs of the occupants. Such operational practices are largely attributed to an increased expectation for stable comfort conditions.
The India specific adaptive model called IMAC developed by CEPT University opens avenues for application of non-conventional cooling technologies for use of buildings in India. These technologies have the potential to provide comfort while requiring relatively lower amounts of operational energy.
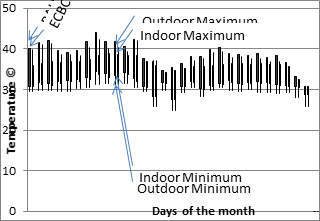
In the absence of space conditioning standard contextual to Indian context, the space conditioning systems for buildings are designed based on ISO and ASHRAE thermal comfort standards. Field observations have indicated that these systems often operate at 22.5 ± 1°C (72.5°F ± 1.8°F) all year round without adjusting to comfort needs of the occupants.
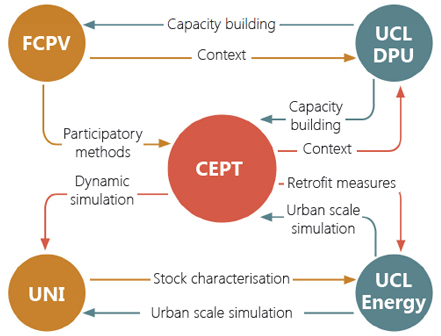
Insecure and informal access to energy impacts on all aspects of life for poor communities living in sub-standard housing in the global South. Access to affordable, reliable and safe forms of energy services has particularly profound effects on health and economic opportunities. However, the ways in which these communities access and use energy in their day-to-day lives are poorly understood.
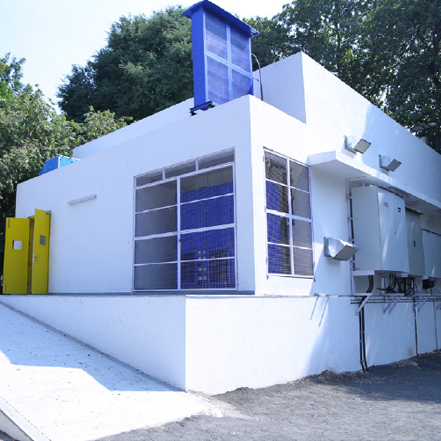

Room Air Conditioners (RACs) are one of the most significant energy loads in modern buildings. With the warming climes and increasing RAC use, typically in the tropics, it was pertinent to address the cooling challenge through a leapfrogging international initiative in the Global Cooling Prize (GCP).

Energy security, climate change and economic growth are matters of international importance which are affecting billions of people globally. One of the most significant global development challenge is how we mitigate against the proliferation of energy intensive air-conditioning (AC) for cooling and ventilation in buildings in response to a globally warming world and the greater expectations for thermal comfort in buildings.
India, with a population of nearly 1.2 billion, is the world’s third-largest greenhouse gas emitter. It has pledged to reduce carbon emission per unit of gross domestic product up to 35% by 2030 from the 2005 level. The building sector is experiencing unprecedented growth leading to higher energy consumption. India’s electricity demand is expected to rise from 775 TWh in 2012 to 2499 TWh by 2030. Estimates by National Institution for Transforming India (NITI Aayog) indicate that the mitigation activities for moderate low carbon development would cost India around USD 834 billion till 2030 at 2011 prices.
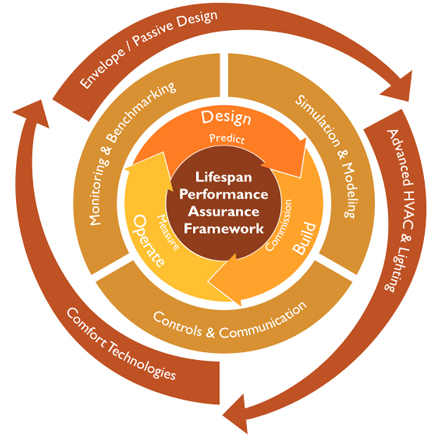
Through the Partnership to Advance Clean Energy (PACE) Research program, a five-year joint U.S. India Center for Building Energy Research and Development (CBERD) was created to advance buildings energy efficiency in both nations.UC Berkeley (USA) and CEPT University (India) jointly proposed the United States–India CBERD program. The main focus of CBERD during the duration of five years (2012-2017) was to conduct collaborative research that results into reduction in energy use in buildings.
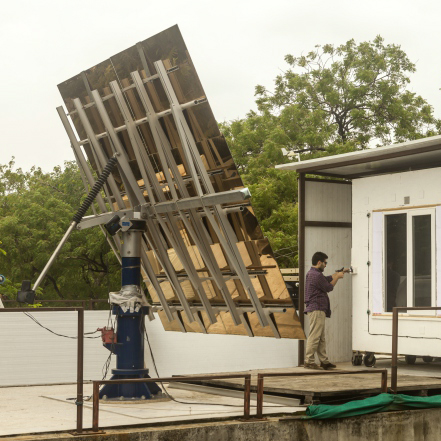

The main aim of the Centre for Excellence in Solar Passive Architecture and Green Building Technologies established at CEPT University with support from Ministry of New and Renewable Energy (MNRE), was to frame strategies for developing energy efficient, low carbon and sustainable built environment using concepts of green architecture and integration of renewable energy systems. The specific objectives for the project duration of five year (2011-2016) were to enhance knowledge and develop a database of construction materials and practices for energy efficient buildings in India.
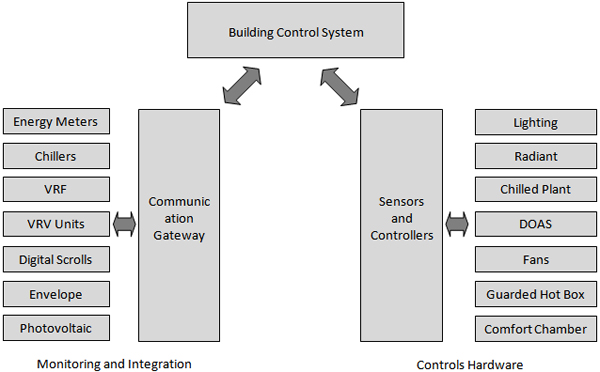
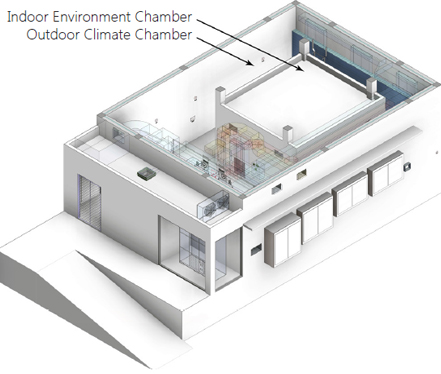
Net-Zero Energy Building (NZEB) is envisioned as a living laboratory for continuous and in-depth building energy-efficiency research. To achieve the goal, building design contains sophisticated and flexible control systems that can support continuous research experiments on building monitoring and performance optimization. The control system in the building is designed to meet the following
Providing daylight in the spaces is crucial for energy conservation as well as health and wellbeing and improved work efficiency of human beings. Tubular Daylighting Devices (TDD – also called Light pipes) are simple means of directing daylight (diffuse and direct light) from the sky into interior spaces and provide natural light in those areas of the building with limited or no access to daylight. TDDs consist of three parts: outside collector, tube to transport daylight and a diffuser inside the room.

Center for Advanced Research in Building Science and Technology (CARBSE) has constructed a Mirror Box to create Artificial Sky conditions. A mirror box is used to simulate overcast sky conditions for building models, which can help architects and engineers to understand daylight inside the building and take necessary design decisions to increase building performance and reduce energy consumption for artificial lighting.

Center for Advanced Research in Building Science and Technology (CARBSE) is constructing Single Patch Sky Simulator which can be used to simulate Artificial Sky. It can create various sky conditions for building models to be analysed, which helps architects and engineers to understand daylighting inside the building and make necessary changes to the design and specifications of glazing to increase building performance and reduce energy consumption for artificial lighting.

Buildings contribute to greenhouse gas emissions more than the industrial or transportation sectors, primarily due to high energy demand and usage in air conditioning, heating and ventilation, driven by the basic human need for thermal comfort and good indoor air quality.
Given India’s rapid economic growth and concomitant expansion in its commercial sector, soaring demand for air-conditioned commercial buildings can be confidently predicted. This increased demand for air-conditioned buildings in India has been attributed to an increased expectation for stable comfort conditions as the workforce shifts away from an industrial production towards a service-orientation that is office-based.
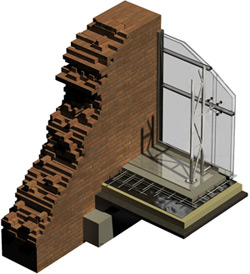
India is experiencing tremendous expansion in Building Construction Industry. Influx of new material has increased in last decade. Building Energy Efficiency and Integration of Renewable Energy Sources has become imperative to meet the global challenges. Building Materials play major role in achieving energy efficiency with the built environment. Number of computer models have been developed and are practiced across the country, which help professionals in envisaging future energy demand within and outside buildings. However, thermo-physical-optical property of locally available building materials is very limited and at the same time, the characterization of newly developed building material is also not very much in public domain. To enhance performance of building material and construction assembly, it is very essential that such knowledge gets created and gets disseminated to all stakeholders.
RACHNA for Practitioners- Brochure
Under the Indo-German Technical Cooperation, the Federal Republic of Germany and the Republic of India jointly agreed to promote the “Indo-German Energy Program” (IGEN). IGEN aims to advance sustainability in the built environment in turn improving environment and climate conditions.
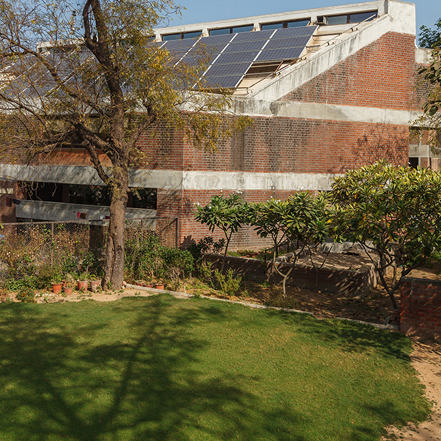

Center for Advanced Research in Building Science and Energy (CARBSE) with support from Bureau of Energy Efficiency (BEE), Ministry of Power Govt of India conducted three day refresher course for the master trainers recognised by BEE for Energy Conservation Building Code.

International Finance Corporation (IFC) and CARBSE conducted two Teachers Training (ToT) Program to train the educators from architecture and engineering higher education institutes. The teachers trained during this program are expected to impart education to the students in their universities to promote awareness and understanding of green buildings IFC has developed a green building course of approximately 20 hours duration, aimed at university students of architecture and engineering and professionals related to sustainable construction.

December 15-22, 2019
The Indo-Swiss Building Energy Efficiency Camp (BEEP Camp) is an intensive and immersive experience, designed to enable learning in the domain of building energy efficiency and the integrated design process.
The urban microclimate modelling is used to understand the effects of extreme weather on the occupant’s thermal comfort

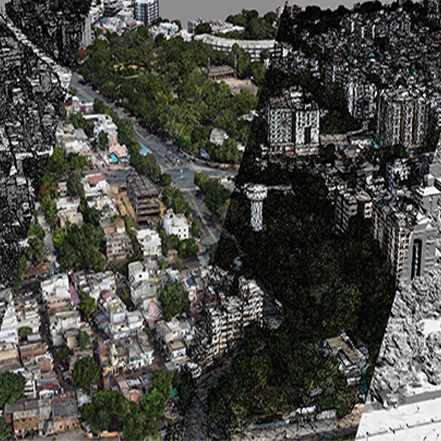
The Equipment consists of an robust hexa-copter with RTK capabilities for high precision position data, which is used with an 5-angle oblique camera which captures detailed aerial images
